TOKYO and CAMBRIDGE, Eisai Co., Ltd. (Headquarters: Tokyo, CEO: Haruo Naito, “Eisai”) and Biogen Inc. (Nasdaq: BIIB, Corporate headquarters: Cambridge, Massachusetts, CEO: Christopher A. Viehbacher, “Biogen”) announced today that the results from Eisai’s large global Phase 3 confirmatory Clarity AD clinical study of lecanemab (development code: BAN2401), an investigational anti-amyloid beta (Aβ) protofibril antibody for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) due to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild AD (collectively known as early AD) with confirmed presence of amyloid pathology in the brain, were presented at the 2022 Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease (CTAD) conference, in San Francisco, California and virtually.
Summary of Presentations in the Scientific Session featuring Lecanemab at CTAD
Design of Clarity AD Study
Eisai’s Clarity AD was a global confirmatory Phase 3 placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group, randomized study in 1,795 people with early AD (lecanemab group: 898 placebo group: 897) at 235 sites in North America, Europe, and Asia. The participants were randomized 1:1 to receive either placebo or lecanemab 10-mg/kg IV biweekly, and the randomization was stratified according to clinical subgroup (MCI due to AD or mild AD), presence or absence of concomitant approved AD symptomatic medication at baseline (e.g., acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, memantine, or both), ApoE4 status and geographical region. Eligibility criteria allowed patients with a broad range of comorbidities/comedications, including but not limited to hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, obesity, renal disease and anti-coagulants. As a result of Eisai’s recruitment strategy of diversity in the Clarity AD study, 4.5% and 22.5% of the randomized participants in the U.S. were Black and Hispanic, respectively.
The primary endpoint was change from baseline at 18 months in the CDR-SB1 (Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes), the global cognitive and functional scale, and key secondary endpoints were the change from baseline at 18 months in amyloid Positron Emission Tomography (PET) using Centiloids, AD Assessment Scale – Cognitive Subscale 14 (ADAS-Cog142), AD Composite Score (ADCOMS3) and AD Cooperative Study-Activities of Daily Living Scale for Mild Cognitive Impairment (ADCS MCI-ADL4). In addition, longitudinal changes in brain tau pathology as measured by tau PET (n=257) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers of AD pathology (n=281) were evaluated in optional sub-studies.
Efficacy Results of Clarity AD
Mean change of CDR-SB from baseline at 18 months as the primary endpoint was 1.21 and 1.66 for lecanemab and placebo groups, respectively. Lecanemab treatment resulted in highly statistically significant results, reducing clinical decline on the global cognitive and functional scale, compared with placebo at 18 months by -0.45 (95% Confidence Interval (CI): -0.67, -0.23; P=0.00005), representing a 27% slowing of decline. Starting as early as six months (difference: -0.17 [95% CI: -0.29, -0.05]; P<0.01), and increasing in absolute difference over time across all time points every 3 months, the treatment showed highly statistically significant changes in CDR-SB from baseline compared to placebo (all p-values are less than 0.01) (Figure 1).
All key secondary endpoints also showed highly statistically significant results compared with placebo (P<0.001). In the amyloid PET sub-study, treatment with lecanemab showed statistically significant reduction in amyloid plaque burden at all timepoints starting at 3 months. Mean change in Centiloids at 18 months was -55.5 and 3.6 for lecanemab and placebo groups, respectively (mean difference: -59.1 [95%CI: -62.6, -55.6]; P<0.00001). Lecanemab slowed decline of cognitive function by 26% on ADAS-Cog14 at 18 months (mean difference: -1.44 [95%CI: -2.27, -0.61]; P=0.00065). In the ADCOMS assessment, lecanemab slowed disease progression by 24% at 18 months (mean difference: -0.050 [95% CI: -0.074, -0.027; P=0.00002]). Lecanemab slowed decline of activities of daily living by 37% on ADCS MCI-ADL at 18 months (mean difference: 2.016 [95%CI: 1.208, 2.823]; P<0.00001). In addition, the primary stratified analysis showed consistent results in CDR-SB, ADAS-Cog14 and ADCS MCI-ADL at 18 months of treatment with lecanemab in all subgroups of disease stage (MCI due to AD or mild AD), ApoE4 status (non-carriers, carriers), presence or absence of concomitant approved AD symptomatic medication, and region (North America, Asia, Europe).
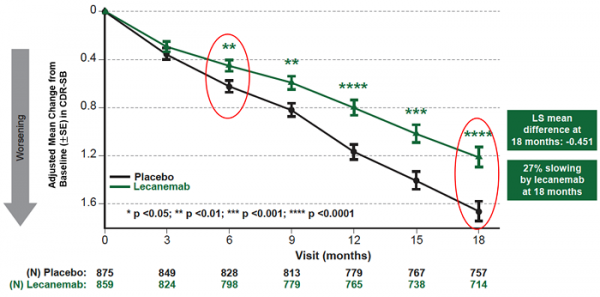
Figure1. CDR-SB as Primary endpoint change (18 months)
Safety Results of Clarity AD
The most common adverse events (>10%) in the lecanemab group were infusion reactions (lecanemab: 26.4%; placebo: 7.4%), ARIA-H (combined cerebral microhemorrhages, cerebral macrohemorrhages, and superficial siderosis; lecanemab: 17.3%; placebo: 9.0%), ARIA-E (edema/effusion; lecanemab: 12.6%; placebo: 1.7%), headache (lecanemab: 11.1%; placebo: 8.1%), and fall (lecanemab: 10.4%; placebo: 9.6%). Infusion reactions were largely mild-to-moderate (grade 1-2: 96%) and occurred on the first dose (75%).
During the study period, deaths occurred in 0.7% and 0.8% of participants in the lecanemab and placebo groups, respectively and no deaths were related to lecanemab or occurred with amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) in 18-month double-blind study period. Serious adverse events were experienced by 14.0% of participants in the lecanemab group and 11.3% of participants in the placebo group. Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 88.9% and 81.9% of participants in the lecanemab and placebo groups, respectively. Treatment-emergent adverse events leading to drug withdrawal occurred in 6.9% and 2.9% of participants in the lecanemab and placebo groups, respectively.
Overall, lecanemab’s ARIA incidence profile was within expectations based on the Phase 2 trial results. ARIA-E events were largely mild-to-moderate radiographically (91% of those who had ARIA-E), asymptomatic (78% of those who had ARIA-E), occurred within the first 3 months of treatment (71% of those who had ARIA-E) and resolved within 4 months of detection (81% of those who had ARIA-E). Among the 2.8% of lecanemab-treated subjects with symptomatic ARIA-E, the most commonly reported symptoms were headache, visual disturbance, and confusion. The incidence of symptomatic ARIA-H was 0.7% in the lecanemab group and 0.2% in the placebo group. No imbalance was observed in isolated ARIA-H (i.e., ARIA-H in participants who did not also experience ARIA-E) between lecanemab (8.9%) and placebo (7.8%). ARIA-E and ARIA-H were less common in ApoE4 non-carriers versus carriers, with higher frequency in ApoE4 homozygous carriers vs ApoE4 heterozygous carriers. In the core study and subsequent open-label extension study, rates of deaths with concurrent cerebral macrohemorrhage were 0.1% in both the placebo group (1/897) and the lecanemab group (2/1608). The two cases on lecanemab occurred in the open-label extension study. Both cases had significant comorbidities and risk factors including anticoagulation contributing to macrohemorrhage or death. Therefore, it is Eisai’s assessment that the deaths cannot be attributed to lecanemab.
Imaging, Plasma, and CSF Biomarkers Assessments of Clarity AD
Biomarkers assessments on amyloid, tau and neurodegeneration with lecanemab administration were conducted using imaging, plasma and CSF. Amyloid biomarkers showed early and sustained amyloid reversal effects in CSF and plasma Aβ 42/40 ratio with lecanemab treatment. Mean amyloid PET was 22.99 Centiloids at 18 months of lecanemab treatment which was below threshold for amyloid positivity of 30 Centiloids. Tau biomarkers showed that removing amyloid improved CSF and plasma p-tau (p-tau181), downstream of amyloid in the AD pathology pathway. Tau PET analysis showed that lecanemab treatment slowed tau accumulation in the temporal lobe as well as improved total tau (t-tau) in compared to the placebo. As for biomarkers of neurodegeneration, lecanemab improved glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in plasma, a marker of astrocyte activation, and neurogranin in CSF, a marker of synaptic dysfunction, improved to normal levels by treatment, while there was no significant difference in neurofilament light chains in CSF or plasma between lecanemab and placebo.
Clarity AD Results in Context
AD is a progressive neurological disorder that severely impacts people living with the condition and their loved ones. With the increased global aging population, AD has become a critical issue for society and healthcare systems. New therapeutic agents that act on the disease pathology are needed. The treatment goals for early AD are to have sustained effects on cognitive function, activities of daily living and psychiatric symptoms, to maintain independence longer by slowing progression of the disease and to improve or maintain quality of life.
In Eisai’s confirmatory Clarity AD study, lecanemab demonstrated consistency of results across scales of cognition and function and subgroups (race, ethnicity, comorbidities). Lecanemab treatment showed 31% lower risk of converting to next stage of disease by Global CDR assessment (Hazard Ratio: 0.69). A slope analysis using CDR-SB based on observed data and extrapolation to 30 months showed that lecanemab takes 25.5 months to reach same level as placebo at 18 months, indicating a 7.5 month slowing of progression. Modeling simulations based on the phase 2 trial data suggest that lecanemab may slow the rate of disease progression by 2.5-3.1 years and has the potential to help people remain in the earlier stages of AD for a longer period of time. In addition, it was shown to maintain the health-related quality of life and reduce the burden on caregivers (23-56% reduction in score worsening). The convergence of evidence across cognition and function, disease progression, health related quality of life, and caregiver burden?demonstrate that?lecanemab?treatment may provide meaningful benefits to patients, their care partners, physicians and society.
Eisai is hosting a live webcast of the scientific session featuring the lecanemab presentations, which can be viewed live on the investors section of the Eisai Co., Ltd. website. The content will be available on demand afterward.
Eisai serves as the lead of lecanemab development and regulatory submissions globally with both Eisai and Biogen co-commercializing and co-promoting the product and Eisai having final decision-making authority.
This release discusses investigational uses of an agent in development and is not intended to convey conclusions about efficacy or safety. There is no guarantee that such an investigational agent will successfully gain health authority approval.
?
1 CDR-SB is a numeric scale used to quantify the various severity of symptoms of dementia. Based on interviews of people living with AD and family/caregivers, qualified healthcare professionals assess cognitive and functional performance in six areas: memory, orientation, judgment and problem solving, community affairs, home and hobbies, and personal care. The total score of the six areas is the score of CDR-SB, and CDR-SB is also used as an appropriate item for evaluating the effectiveness of therapeutic drugs targeting the early stages of AD.
2 ADAS-Cog is the most common cognitive assessment instrument used in AD clinical trials all over the world. ADAS-Cog14 consists of 14 competencies: word recall, commands, constructional praxis, object and finger naming, ideational praxis, orientation, word recognition, remembering word recognition instructions, comprehension of spoken language, word finding difficulty, spoken language ability, delayed word recall, number cancellation, and maze task. ADAS-Cog has been used in clinical trials for earlier stages of AD including MCI.
3 Developed by Eisai, ADCOMS combines items from the ADAS-Cog scale for assessing cognitive functions, MMSE and the CDR scale for evaluating the severity of dementia to enable highly sensitive detection of changes in clinical functions of early AD symptoms and changes in memory
4 ADCS MCI-ADL assesses the competence of patients with MCI in activities of daily living (ADLs), based on 24 questions to the patient’s partner about actual recent activities of daily living.

微信截圖_16715201564604-600x502.png)

微信截圖_16697882687482-600x517.png)
